Compare the 1796 Election with the 1800
Election:
|
President John Adams was facing
a tough re-election battle. John Adams had been
controversial presidency. His support of the Alien and Sedition Acts, which
were his attempt to silence political opposition, had been met with
serious resistance. John Adams even used these acts against Jefferson's campaign!
Many voters were skeptical about using the new army
to go to war against France after the French Revolution. The Federalists
were also divided between supporting John Adams and Alexander
Hamilton. Into this gap stepped the Democratic-Republican opposition
through Thomas Jefferson. After a slew of personal attacks between
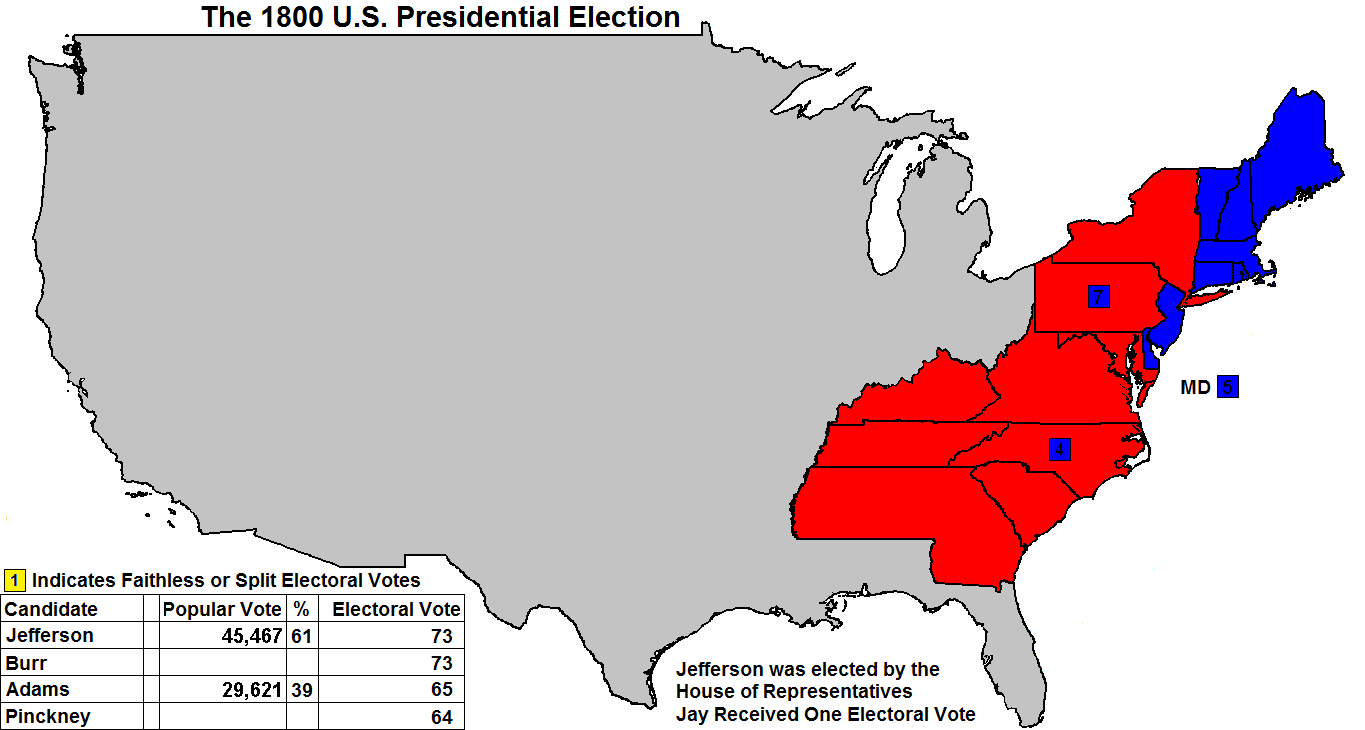
the candidates in their 1800 rematch, Jefferson prevailed. However,
he did tie Aaron Burr in the electoral vote.
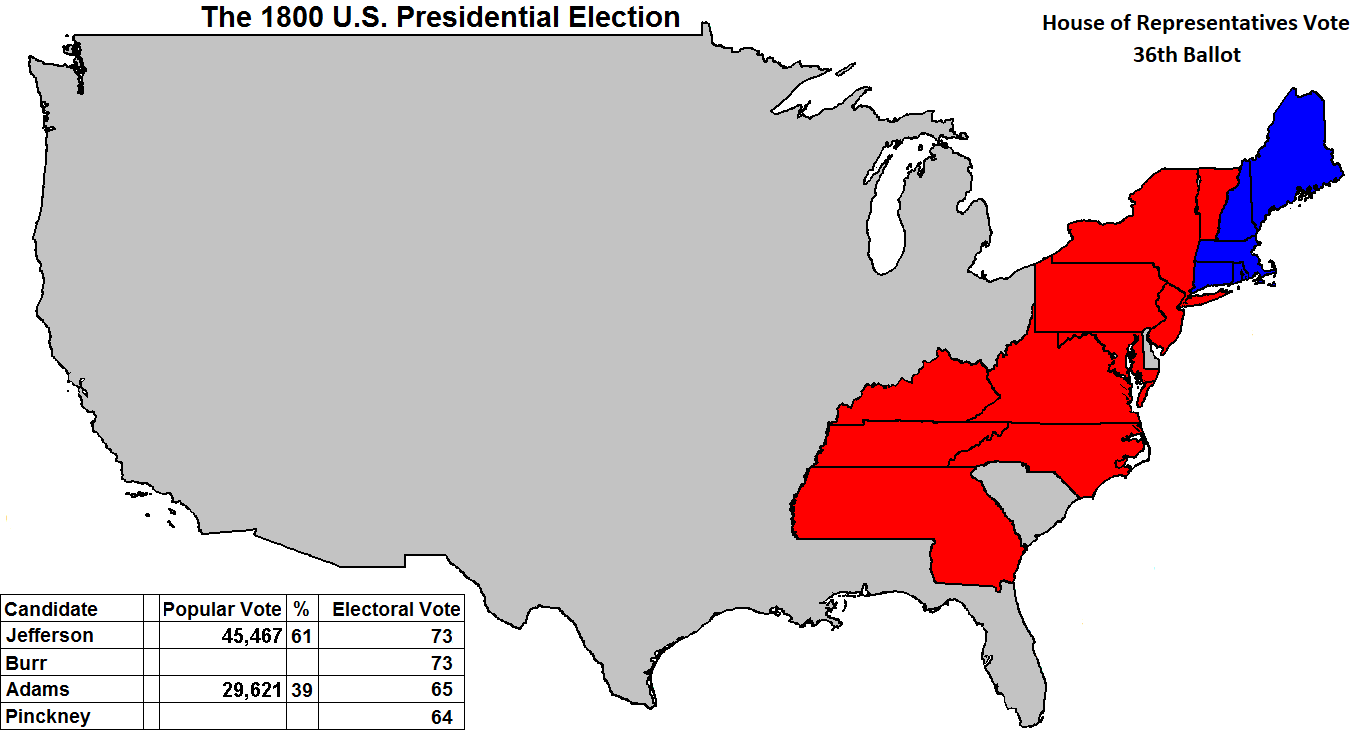
Due to the tie between Thomas Jefferson and Aaron Burr, the House of
Representatives was called upon to elect the president for the first
time in U.S. history. After many tie votes, the House elected Jefferson on the 36th ballot! Alexander Hamilton, an old rival of Jefferson,
decided that he didn't trust Aaron Burr to be President. He
convinced some Congressmen not to vote, which broke the deadlock in
favor of Jefferson. Following the election, the twelfth
amendment to the United States Constitution was ratified as a result
to compel the President and Vice-President to be elected on tickets,
rather than than the original system, where every elector voted for
two candidates and the first place winner was President and the
second place winner was Vice-President.
|
| UNITED STATES |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
 |
45,467 |
61 |
73 |
 Aaron Burr
Aaron Burr |
-- |
-- |
73 |
 John Adams*
John Adams* |
29,621 |
39 |
65 |
 Charles Pinckney
Charles Pinckney |
-- |
-- |
64 |
 John Jay
John Jay |
-- |
-- |
1 |
| The House of
Representatives voted 10-5 on the 36th ballot to elect Thomas
Jefferson as President of the United States. Aaron Burr became
Vice-President. |
| CONNECTICUT |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 John Adams*
John Adams*
 |
No Popular Vote |
-- |
9 |
| DELAWARE |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 John Adams*
John Adams*
 |
No Popular Vote |
-- |
3 |
| GEORGIA |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
 |
No Popular Vote |
-- |
4 |
| KENTUCKY |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
 |
119 |
100 |
4 |
| MARYLAND |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
 |
10,638 |
51 |
5 |
 John Adams*
John Adams* |
10,068 |
49 |
5 |
| MASSACHUSETTS |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 John Adams*
John Adams*
 |
No Popular Vote |
-- |
16 |
| NEW HAMPSHIRE |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 John Adams*
John Adams*
 |
No Popular Vote |
-- |
6 |
| NEW JERSEY |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 John Adams*
John Adams*
 |
No Popular Vote |
-- |
7 |
| NEW YORK |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
 |
No Popular Vote |
-- |
12 |
| NORTH CAROLINA |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
 |
11,593 |
51 |
8 |
 John Adams*
John Adams* |
11,025 |
49 |
4 |
| PENNSYLVANIA |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
 |
No Popular Vote |
-- |
8 |
 John Adams*
John Adams* |
No Popular Vote |
-- |
7 |
| RHODE ISLAND |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson |
2,159 |
48 |
0 |
 John Adams*
John Adams*
 |
2,353 |
52 |
4 |
| SOUTH CAROLINA |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
 |
No Popular Vote |
-- |
8 |
| TENNESSEE |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
 |
No Data |
-- |
3 |
| VERMONT |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 John Adams*
John Adams*
 |
No Popular Vote |
-- |
4 |
| VIRGINIA |
VOTES |
PERCENT |
ELECTORAL VOTE |
 Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
 |
21,002 |
77 |
21 |
 John Adams*
John Adams* |
6,175 |
23 |
0 |

|




